Federal Minister of Innovation, Science and Economic Development Navdeep Bains, announced an investment September 19 of over $39.6 million in 14 innovative clean technology projects across Canada.
The projects, which are being carried out in British Columbia, Manitoba, Ontario and Quebec, span several sectors, including waste management; energy, exploration and production; power generation; energy utilization; and agriculture. Minister Bains also announced $5.5 million in new funding for three previously funded Sustainable Development Technology Canada (SDTC) projects.
Projects are funded through SDTC’s SD Tech Fund. The Government of Canada has allocated a total of $915 million for the fund to invest in pre-commercial Canadian clean technology projects that have the potential to meet market demand and to achieve Canada’s environmental and economic goals in priority areas.
Among the projects are:
• A project by Opus One Solutions Energy Corporation is designed to demonstrate a smart and integrated transactive energy (TE) network that will allow distributed energy resource (DER) technologies, like solar photovoltaic, small-scale renewable and non-renewable generation, energy storage, controllable loads and grid-connected microgrids, to be integrated technically and financially into electric power systems. A suite of software tools, referred to as GridOS, have been developed to efficiently and optimally connect the various components of the grid together, creating a TE network that uses technical and economic signals to manage the exchange of electricity within an electric power system.
The project will demonstrate a TE network for Emera Nova Scotia Power in a feeder-based microgrid (featuring wind resources and a residential microgrid), at Emera Maine’s control and operating system, and at Toronto Hydro’s energy monitoring and control centre.
 e-Zn's reactor design
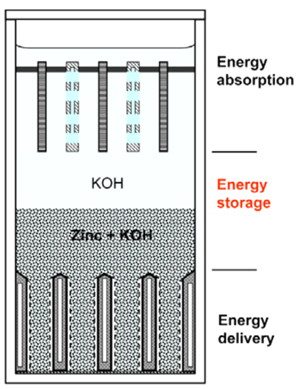
• Toronto-based e-Zn has developed an electrochemical reactor technology for storing electrical energy more economically than conventional designs, using inexpensive zinc. With a price competitive with the least expensive forms of bulk energy storage, e-Zn says its design offers superior flexibility of scale and deployment. The e-Zn reactor is structured with three distinct sections, for energy absorption (charging), energy delivery (discharging) and energy storage. The company says its technology offers many advantages over conventional rechargeable batteries, including a low cost of capacity scaling, an inherently long life with no capacity fading and improved safety.
e-Zn's reactor design
• Toronto-based e-Zn has developed an electrochemical reactor technology for storing electrical energy more economically than conventional designs, using inexpensive zinc. With a price competitive with the least expensive forms of bulk energy storage, e-Zn says its design offers superior flexibility of scale and deployment. The e-Zn reactor is structured with three distinct sections, for energy absorption (charging), energy delivery (discharging) and energy storage. The company says its technology offers many advantages over conventional rechargeable batteries, including a low cost of capacity scaling, an inherently long life with no capacity fading and improved safety.
As part of this project, e-Zn will scale up its 20-watt/500 kilowatt-hour prototype reactor to a demonstration-level, energy storage system rated at one kilowatt/24 kilowatt-hours.
• Schneider Electric’s SmartESS (Smart Energy Storage Solution) platform is a transformer-less, all-in-one, wall-mounted inverter combining a hybrid battery and solar photovoltaic (PV) inverter. The platform has been designed to address the power and energy needs of residences, small commercial businesses, off-grid communities and energy service providers. It integrates solar PV panels, lithium-ion energy storage batteries, and home electricity usage control and monitoring with a utility interface that provides visibility to the local utility and enables smart-grid functionality.
For this project, Schneider Electric—with consortium partner Rainforest Automation providing cloud connection services—is proposing the development and demonstration of SmartESS on the T’Sou-ke First Nation, on the south shore of British Columbia’s Vancouver Island. The project is targeting an integrated solution with inverter, lithium-ion battery storage, balance-of-system, and communication technology that provides increased performance, reliability, and simplicity at a cost lower than existing solutions.
