Washington: The United States solar industry is more than 60% of the way to achieving cost-competitive utility-scale solar photovoltaic electricity, the US Energy Department announced February 12.
In 2011, the Energy Department launched its SunShot Initiative to make solar energy cost-competitive with traditional energy sources by the end of the decade. Through partnerships with industry, universities, local communities and the Department’s national laboratories, the initiative is working to drive innovation and lower the cost of solar energy – from more efficient, high-performing solar modules to streamlined permitting, installation and interconnection processes.
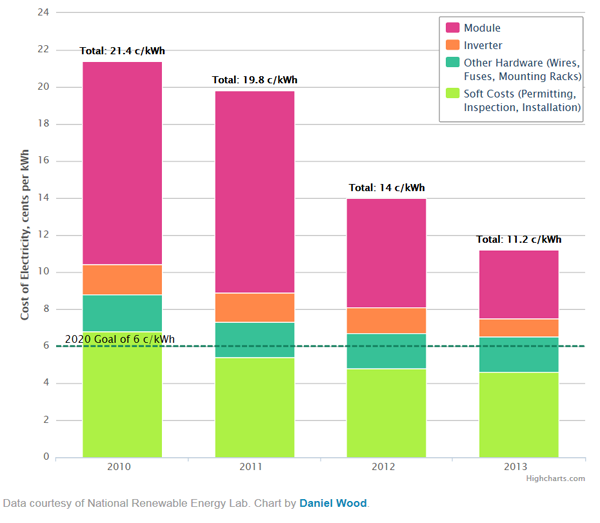
Today, the utility-scale PV industry is more than 60 percent of the way to achieving SunShot’s target of $0.06 per kilowatt-hour, the DOE says. In the United States, the average price for a utility-scale PV project has dropped from about $0.21 per kilowatt-hour in 2010 to $0.11 per kilowatt-hour at the end of 2013. According to the Energy Information Administration, the average U.S. electricity price is about $0.12 per kilowatt-hour. A recent graph from the US government shows how these costs have fallen in the last three years.
The same day, the Energy Department announced $25 million in new funding to boost domestic solar manufacturing and speed up the commercialization of efficient, affordable PV and CSP technologies. This funding opportunity is expected to help to further lower the cost of solar electricity, support a growing U.S. solar workforce and increase U.S. competitiveness in the global clean energy market. Over the last three years, advocates say the cost of a solar energy system has dropped by more than 50 percent.
The Energy Department’s SunShot Initiative aims to make solar energy fully cost-competitive with traditional sources of energy by 2020.
Reductions in the cost of electricity are based on estimates of the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE). The LCOE is a measure of the national average of electricity cost based on certain assumptions regarding financing costs and generation availability projected over the life of a generating asset. The LCOE model provides a benchmark for measuring relative changes in electricity costs.
